Anaplasmosis is a tick bite illness caused by the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum. It is spread by the bite of infected blacklegged ticks, the same tick that transmits Lyme disease, babesiosis, hard tick relapsing fever, and Powassan virus. It is also possible for Anaplasma phagocytophilum to be transmitted through blood transfusions and organ transplants.
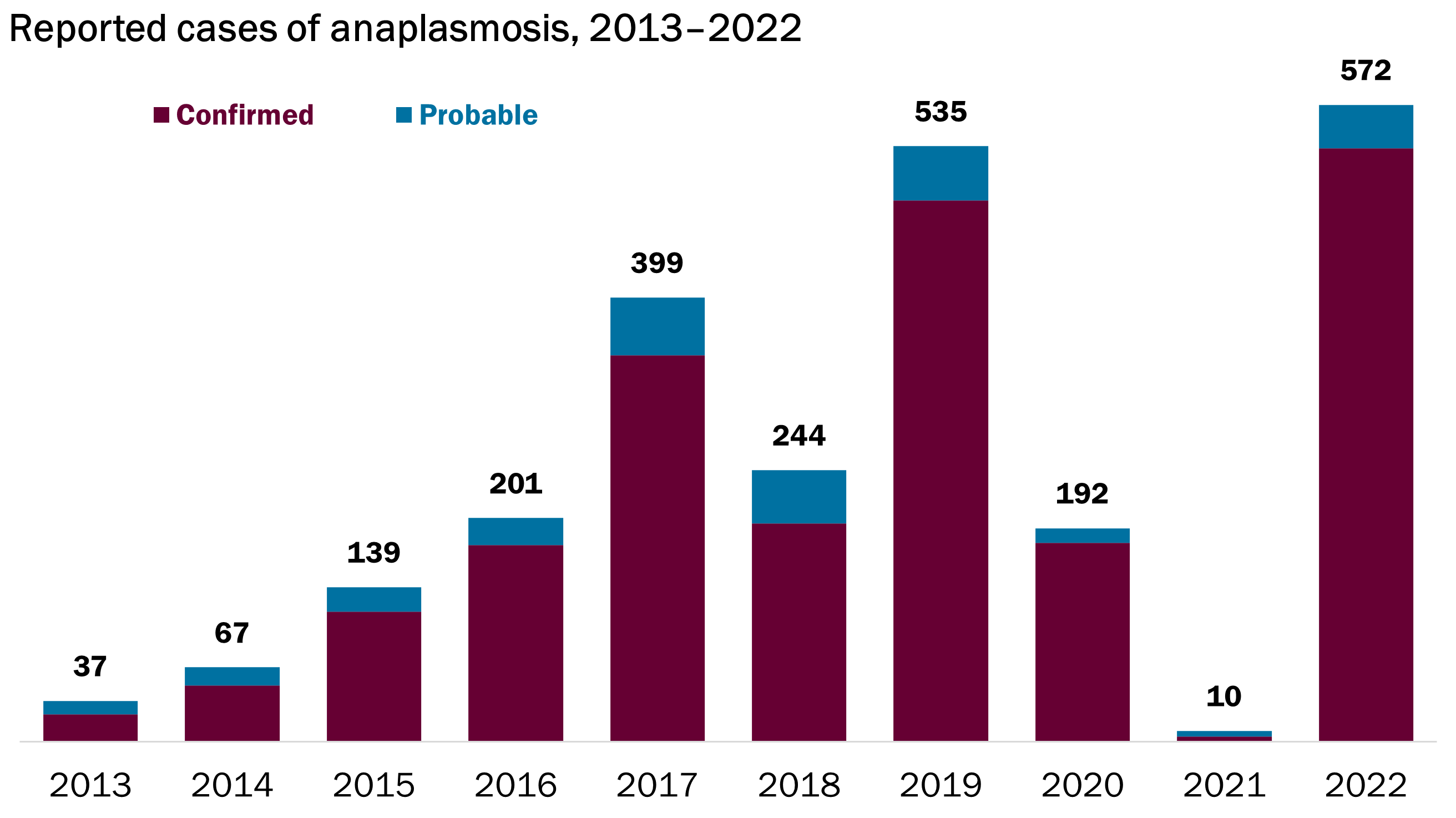
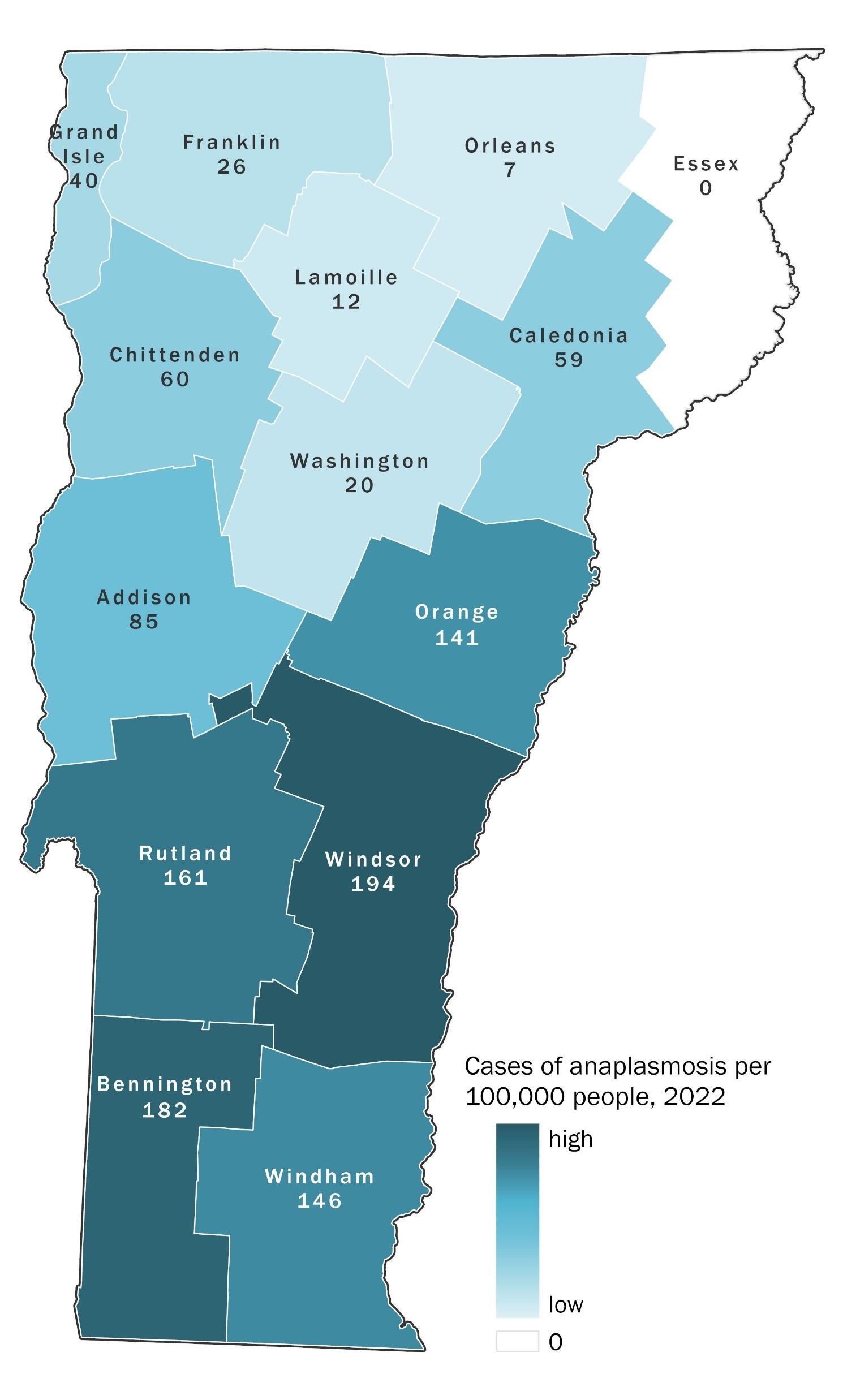
Anaplasmosis is the second most common tick bite illness in Vermont. In the last five years, the number of reported anaplasmosis cases has increased substantially. Since 2015, Vermont has had the highest annual incidence of anaplasmosis in the U.S.
The best way to prevent anaplasmosis is to prevent tick bites. If you find a tick on your body, remove it quickly to reduce the risk of anaplasmosis and other tick bite illnesses. See a health care provider if you get sick. Anaplasmosis is treatable but it can be a serious and sometimes fatal disease.
Explore Anaplasmosis Trends
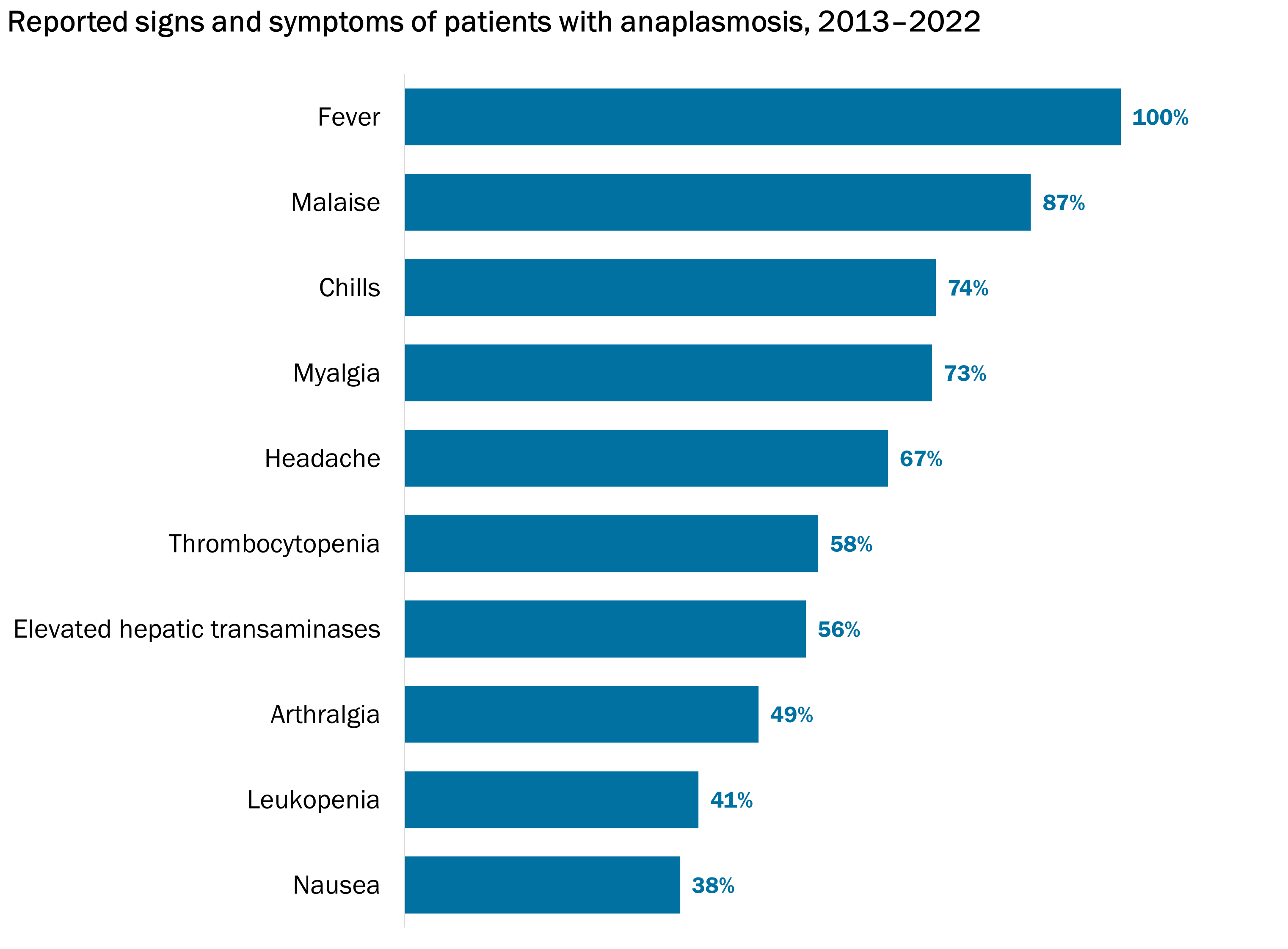
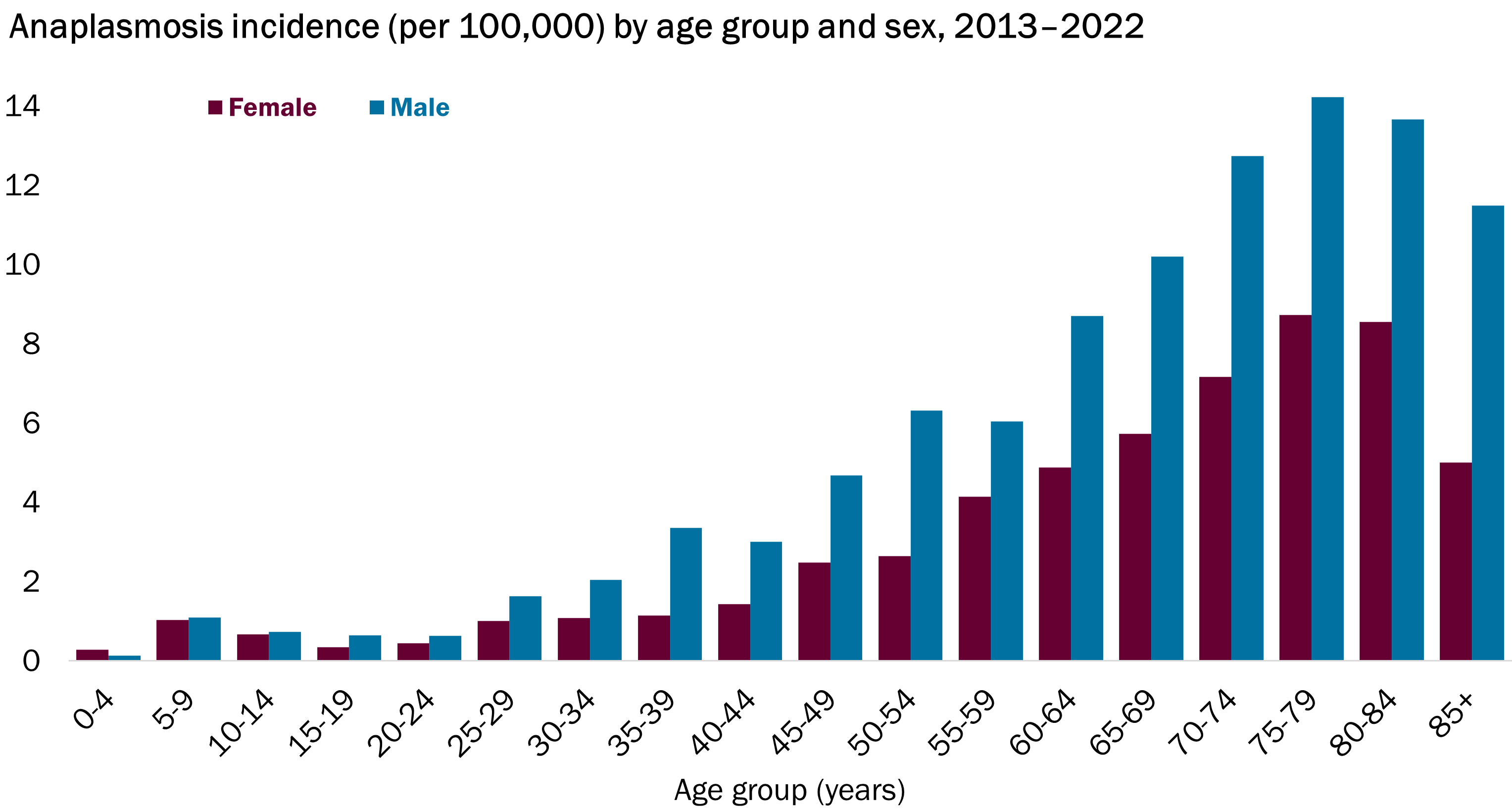
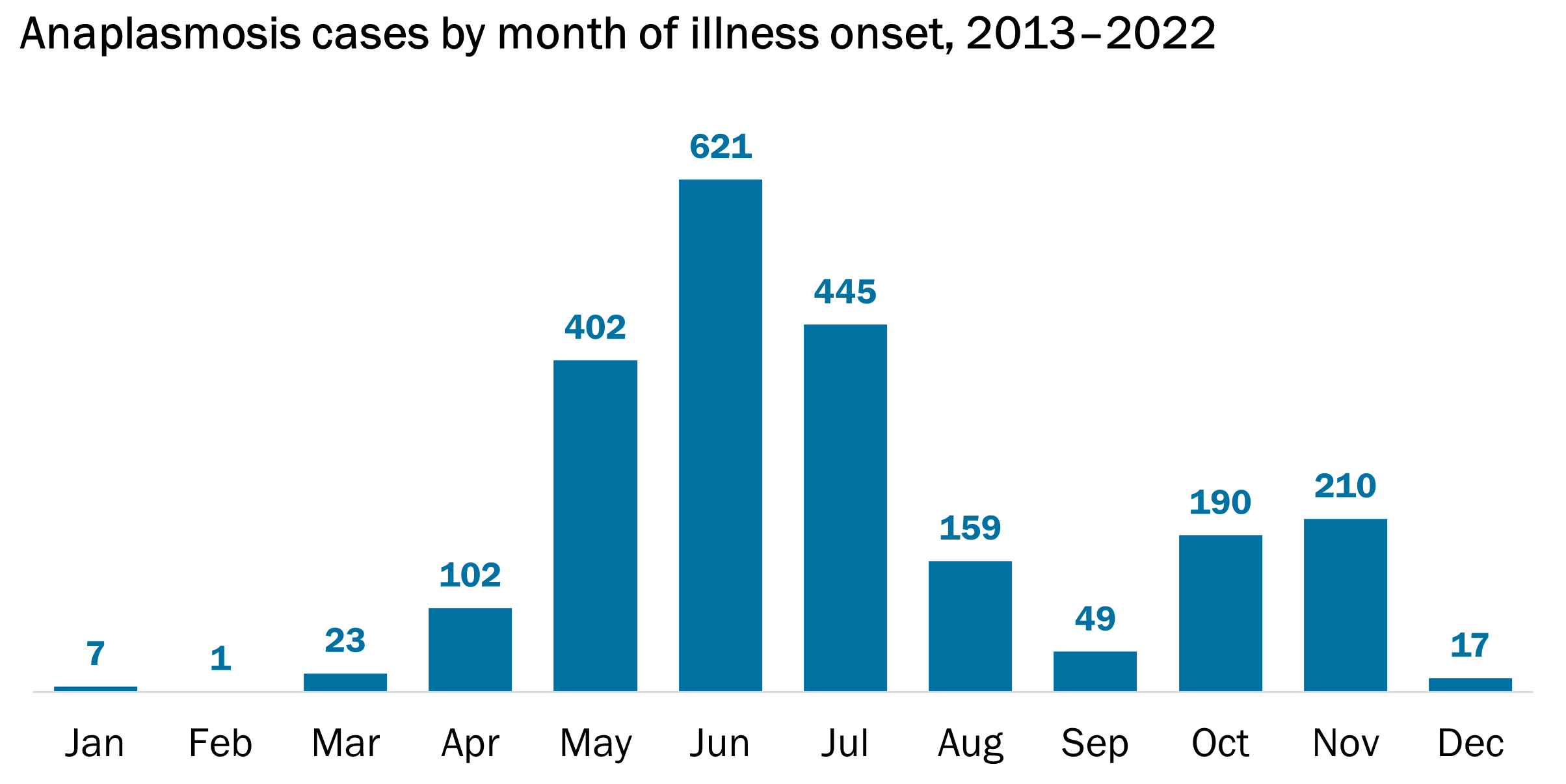
Anaplasmosis is reportable in Vermont. We collect and analyze data on anaplasmosis cases to keep Vermonters informed of their risk so they can take necessary precautions. See below for more information about common symptoms, cases over time, who gets anaplasmosis, and when and where the risk is highest in Vermont.