Stimulant misuse can mean using illicit stimulants (such as cocaine or methamphetamine) or using prescription medication (such medication to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) like Dexedrine®, Adderall®,Ritalin® and Concerta®) as in higher amounts, more often, or for longer than prescribed; using for recreational purposes; or using prescription medication prescribed to someone else. Stimulant misuse can cause serious health effects, addiction, and death.
Vermont's past year stimulant use rates are higher that the U.S. average
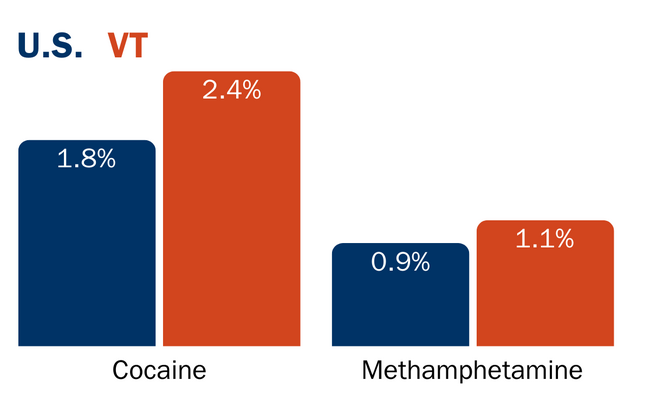
Source: State Level Data National Survey on Drug Use and Health 2022-2023
Health risks of stimulant use
| Short-Term Effects | Long-Term Effects |
|---|---|
|
|
Learn more at NIDA (National Institute on Drug Abuse).

