Addressing opioid overdose takes a comprehensive and holistic approach
Opioids – such as prescription painkillers and heroin – are powerful drugs that are highly addictive. Opioids slow breathing and heartbeat, and act on the brain to relieve pain. They can rewire brain chemistry, making anyone susceptible to addiction. Opioid use disorder (OUD) can have potentially devastating consequences for people who experience addiction and for their families and our communities.
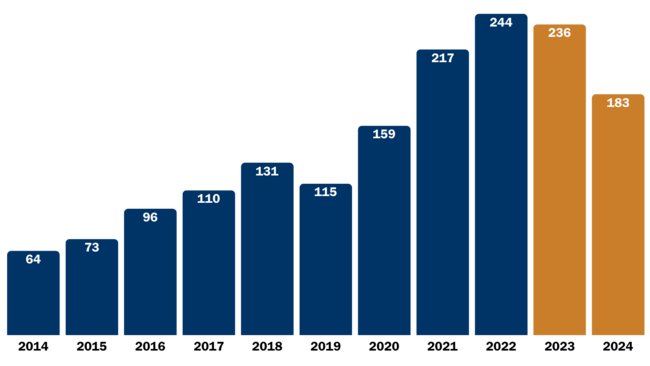
In Vermont, after a decade of steady increases in the number of deaths due to opioid overdose, deaths have started to decrease.